Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a medical term to define a long-term medical condition referred to by the gradual loss of kidney function over time. The kidneys play a very important role in filtering waste and excess fluids from the blood, regulating electrolyte balance, and producing hormones that help control blood pressure and stimulate red blood cell production. This medical condition (CKD) may lead to kidney failure if left untreated. Treatment for chronic kidney disease is also possible with Ayurveda.
Stage 1: GFR (mL/min) 90 and higher - It indicates that kidney function is still relatively normal.
Stage 2: GFR (mL/min) 60 to 89 - It indicates the signs of mild kidney damage.
Stage 3a: GFR (mL/min) 45 to 59 - It indicates mild to moderate kidney damage.
Stage 3b: GFR (mL/min) 30 to 44 - It indicates moderate kidney damage.
Stage 4: GFR (mL/min) 15 to 29 - It indicates severe kidney damage and and close to not functioning.
Stage 5: GFR (mL/min) Less than 15 - It indicates that kidneys have stopped functioning or are very close to failing.
Chronic kidney Disease Treatment is different at each stage.
Causes of Chronic kidney disease include:
Glomerulonephritis: This type of Kidney Disease is characterized by inflammation of the glomeruli, which are the tiny filters in the kidneys responsible for removing waste and excess fluids from the blood to form urine.
Polycystic kidney disease: PKD is a genetic disorder characterized by the growth of numerous cysts (fluid-filled sacs) in the kidneys. These cysts decrease the ability of kidney function over time.
Membranous nephropathy: Membranous nephropathy is a type of kidney disorder characterized by the thickening of the glomerular membrane, which is part of the kidney's filtration system. This thickening occurs due to the deposition of immune complexes and other substances, leading to impaired kidney function.
Obstructions of the urinary tract: From cancer, enlarged prostate, or kidney stones.
Vesicoureteral reflux: It is a medical term to define a medical condition where urine flows backward from the bladder into the ureters (one or both) and sometimes into the kidneys. Normally, urine flows from the kidneys to the bladder through the ureters, and then out of the body through the urethra during urination.
Nephrotic syndrome: Nephrotic syndrome is a medical term to define a kidney disorder characterized by a collection of symptoms that indicate kidney damage.
Pyelonephritis: Pyelonephritis is a type of urinary tract infection (UTI) that involves inflammation of the kidney(s).
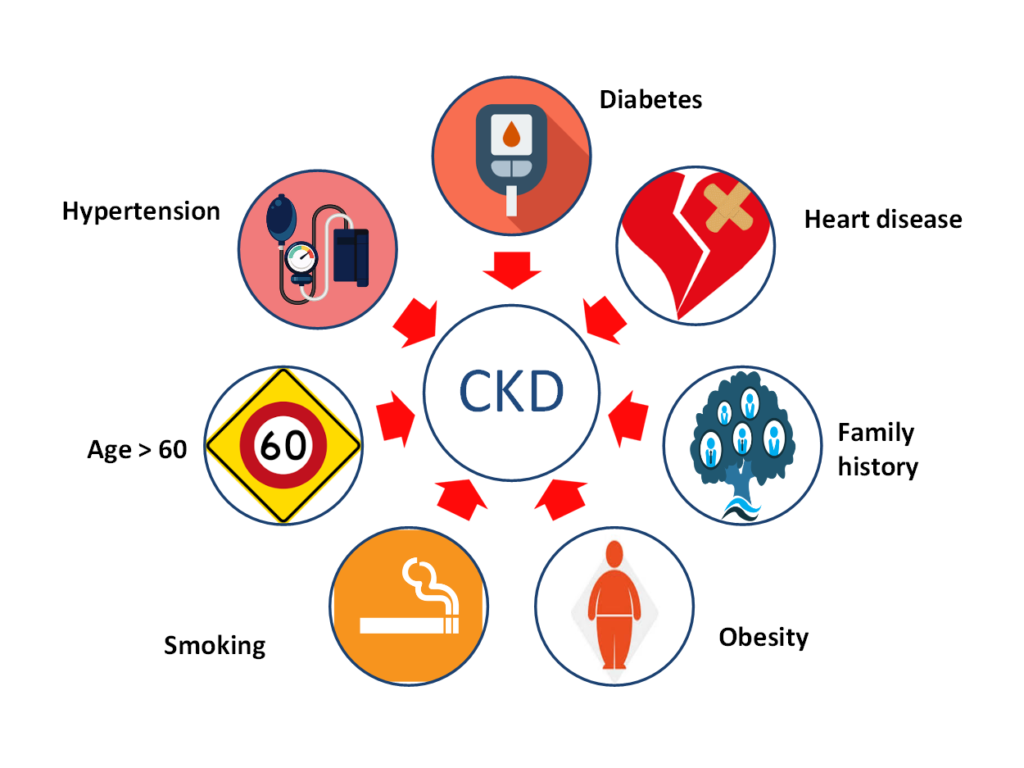
High blood pressure (hypertension): High blood pressure (hypertension) is a significant risk factor for chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Diabetes: Diabetes is one of the leading causes of chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Diabetes-related nephropathy: It is a serious complication of diabetes mellitus that affects the kidneys. It is one of the leading causes of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and end-stage kidney disease (ESKD).
Lupus and other immune system disorders including sarcoidosis, polyarteritis nodosa, Goodpasture syndrome, and Henoch-Schönlein purpura can cause kidney problems.
Early stages of chronic kidney disease usually do not show symptoms. As the CKD (Chronic Kidney Disease) worsens symptoms may include:
Once your body shows any of these symptoms then you should get treatment for chronic kidney disease.
CKD can happen to anyone. But you will be more at risk if you have:
The diagnosis of chronic kidney disease (CKD) involves past medical records, physical examinations, laboratory tests, and imaging studies.
1. Blood tests serum creatinine level: A blood test to measure the level of creatinine, a waste product produced by muscle metabolism. High creatinine levels can indicate decreased kidney function.
2. Urine tests: Urinalysis to assess for proteinuria (presence of protein in the urine), hematuria (presence of blood in the urine), and other abnormalities. The urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR) may also be measured to quantify proteinuria.
3. Imaging tests: such as ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or CT scan.
4. Blood tests (eGFR): determined based on serum creatinine, age, gender, and race. eGFR provides an estimate of kidney function and helps classify CKD into stages.
If you are a resident of Delhi, chronic kidney disease treatment in Delhi including diagnosis is available in many clinics and hospitals.
Complications of chronic kidney disease include:
Gout: Gout is a form of arthritis characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in the joints, often affecting the big toe. It occurs due to the accumulation of urate crystals (needle-shaped crystals) in the joints, which form when there is a high level of uric acid in the blood (hyperuricemia).
Metabolic acidosis: It is a medical condition characterized by a chemical imbalance in your blood due to a decrease in kidney function.
Heart disease and Arteries disease: It involves an increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
Nerve damage: It is also known as neuropathy, which refers to a condition where the peripheral nerves are damaged, resulting in various symptoms such as pain, numbness, tingling, weakness, or loss of sensation in the affected area.
Hyperkalemia: is a medical condition referred to by high levels of potassium in the blood. This medical condition may affect the heart’s ability to function properly.
Hyperphosphatemia: High phosphorus
Anemia: Anemia is a condition characterized by a deficiency in red blood cells or hemoglobin, resulting in reduced oxygen-carrying capacity in the blood.
Infections: A weak immune system increases the risk of infections.
Fluid buildup: This leads to swelling in your leg, ankles, hands and feet.
Chronic kidney disease treatment in Delhi is available in many hospitals.

Regular health checkup is a good habit for preventing CKD.
If you are a resident of Delhi, there are many options for chronic kidney Disease treatment

Certificate no- AH-2023-0186
JAN 05,2023-JAN 04,2026
"Ayurveda is not just a system of medicine; it's a way of life. Connect with us to embrace a lifestyle that nurtures your body, mind, and soul."
Book Consultation Now